Profit and Loss Definitions, Formulas, Solved Problems
Basic Definitions and Formulas
- Cost price (C.P.): This is the price at which an article is purchased.
- Selling price (S.P.): This is the price at which an article is sold.
- Profit or Gain: If the selling price is more than the cost price, the difference between them is the profit incurred.
Formula: Profit or Gain = S.P. – C.P.
- Loss: If the selling price is less than the cost price, the difference between them is the loss incurred.
Formula: Loss = Cost price (C.P.) – Selling Price (S.P.)
- Profit or Loss is always calculated on the cost price.
- Marked price: This is the price marked as the selling price on an article, also known as the listed price.
- Discount or Rebate: This is the reduction in price offered on the marked or listed price.
Below is the list of some basic formulas used in solving questions on profit and loss:
- Gain % = (Gain / CP) * 100
- Loss % = (Loss / CP) * 100
- SP = [(100 + Gain%) / 100] * CP
- SP = [(100 – Loss %) / 100]*CP
The above two formulas can be stated as,
If an article is sold at a gain of 10%, then SP = 110% of CP.
If an article is sold at a loss of 10%, then SP = 90% of CP.
- CP = [100 / (100 + Gain%)] * SP
- CP = [100 / (100 – Loss%)] * SP
IMPORTANT FORMULAE
- Gain = (S.P.) - (C.P.)
- Loss = (C.P.) - (S.P.)
- Loss or gain is always reckoned on C.P.
- Gain Percentage: (Gain %)
Gain % = 
Gain x 100 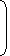
C.P. - Loss Percentage: (Loss %)
Loss % = 
Loss x 100 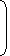
C.P. - Selling Price: (S.P.)
SP = 
(100 + Gain %) x C.P 
100 - Selling Price: (S.P.)
SP = 
(100 - Loss %) x C.P. 
100 - Cost Price: (C.P.)
C.P. = 
100 x S.P. 
(100 + Gain %) - Cost Price: (C.P.)
C.P. = 
100 x S.P. 
(100 - Loss %) - If an article is sold at a gain of say 35%, then S.P. = 135% of C.P.
- If an article is sold at a loss of say, 35% then S.P. = 65% of C.P.
- When a person sells two similar items, one at a gain of say x%, and the other at a loss of x%, then the seller always incurs a loss given by:
Loss % = 
Common Loss and Gain % 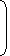
2 = x 2 . 10 100 - If a trader professes to sell his goods at cost price, but uses false weights, then
Gain % = 
Error x 100  %.
%.(True Value) - (Error)
Basic Questions:
1 Man buys card for Rs 2000 & sells it for 2500 what will be gain%
2 Man buys pan for Rs 1400 & sells at loss of 15% What is SP
3 By selling mobile for Rs 2400 a shopkeeper make 25% profit.what will be profit % if he had sold it for Rs 2040
4 The owner of a bookshop charges his customer 23% more than the cost price. If a customer paid Rs 7011 for a book then what was the cost price of the book.
5 man sells an article for Rs 2700 & he losses 10% at what price he should sell to gain 5%
6 Man bought an article for Rs 4000 & sold it for 35% profit from that amount he purchased another article & sold at loss of 20% what is total profit or loss ?
7 A bought banana for Rs 60 per Dozen what is selling price per 100 to get gain of 12%
8 The CP of an item is two third of its SP. what is gain or loss % on that time?
Practice questions
1. at what % above the CP must be marked to gain 33% after allowing discount of 5%
Answer: 40%
2. A shopkeeper earns 20% profit on the selling price. What is his profit percentage on the cost price
Answer: 25%
3. A merchant finds that the cost price of 2750 apples is the same as the selling price of 2500 apples. The loss or gains percent is
Answer: 10% gain
4. The loss percent incurred when an object is sold at Rs 436 is equal to the profit percent which is gained if the object is sold at Rs 464. Find the selling price to get a profit of 10%
Answer: Rs 495
6.A shopkeeper sells an article for Rs 78 and earns double the profit that he would have earned had he sold it for Rs 69.What is the cost price ?
Answer: Rs 60
7. A man buys pencils at the rate of 6 for Rs 5 and sells them at 5 fo Rs 6. His profit percent is
Answer: 44%
8.Some toffees were bought at the rate fo 11 for Rs 10 and the same number at the rate of 9 for Rs 10. If the whole lot was sold at one rupee per toffee, then gain or loss in the whole transaction was
Answer: 1% loss
9.By selling 33m cloth a shopkeeper earns profit equivalent to selling price of 11m. Find his profit percentages?
Answer: 50%
10. By selling 33 m cloth, a shopkeeper loss money equivalent to selling price of 11m. Find his loss percentage
Answer: 25 %
11. By selling 33m cloth a shopkeeper earns profit equivalent to the cost price of 11 m. Find his selling profit percentage.
Answer: 33.33%
12. The cost price of 20 article is same as the selling price of 10 articles. The profit percent is
Answer: 100%
13.A dealer sold two bikes for Rs 7400 each. On one he gained 10% and on the other he lost 10%. The dealer's loss or gain in the transactions is
Answer: 1% loss
14. A dishonest shopkeeper sells goods at cost price but uses 800 gms in place of 1 Kg weight. Find his profit percent
Answer: 25%
15. The price of tea increases by 32% and so a housewife expenditure on tea increases by 10%. If she bought 10 kg earlier, what is the quantity bought now.
Answer: 8.33
16. A shopkeeper sells an article at 20% profit. Had he bought it for 10% less and sold it fo Rs 12 less, he would have earned 30% profit. What is the actual costs price.
Answer: Rs 400
17. A persons sells an article at a profit of 10%. If he had bought it at 10% less and sold it for Rs 3 more, he would have gains 25%. Find the cost price.
Answer:Rs 120
18. Mohit sold an article for Rs 1840 and made Rs 15 percent profit on the discounted price he bought. If the discount was 20% , what was the original price?
Answer: Rs.2000
19. A sold an article to B at the profit of 25%, B sold it to C at loss of 10% and C sold it to D at the profit of 20%. If D paid Rs 27 then how much A paid to buy article?
Answer:Rs 20
20. A person bought two watches for Rs 480. He sold one at a loss of 15% and the other at a profit of 19% and he found that each watch was sold at the same price.Find the cost price of two watches
Answer: Rs 280, Rs 200
21. At the marked price of 36 pens a retail seller buys 40 pens. If he gives 1% discount, find his profit percent
Answer: 105
22. 9 kg of rice cost as much as 4kg of sugar, 14 kg of sugar cost as much as 1.5 Kg of tea, 2 kg of tea cost as much as 5 kgs of coffee; find the cost of 11 kgs of coffee, if 2.5 kg of rice cost 12.50
Answer: Rs 462
23. A man buys some oranges at the rate of 5 for 1 and same number fo oranges at the rate of 4 for Rs 1. He sold all of them at the rate of 9 for Rs 2. During the whole transactions, he incurred a loss of Rs 30. Find the number of articles that he purchased.
Answer: Rs 10800
24. A shopkeeper promises to sell his goods at 10% profit but he uses a false weight of 205 less. Find his profit%
Answer: 37.5
25. A man purchases some oranges at the rate of 25 for 1. How many for Rs 1 should he sell to gain 25% profit.
Answer: 20
26. By selling 32 toffees for Rs 1 a man loses 40%. How many for Rs 1 did he sell to gain 20% profit
Answer:16
27. The profit % of A and B are same on selling the articles at Rs 1800 each but A calculated his profit on selling price and B calculated his profit on cost price which is equal to 20%.Find the total C.P
Answer: 2940
28. At what % above the C.P must an article be marked so as to gain 33% after allowing a customer a discount of 5%
Answer: 40%
Answer: 40%
2. A shopkeeper earns 20% profit on the selling price. What is his profit percentage on the cost price
Answer: 25%
3. A merchant finds that the cost price of 2750 apples is the same as the selling price of 2500 apples. The loss or gains percent is
Answer: 10% gain
4. The loss percent incurred when an object is sold at Rs 436 is equal to the profit percent which is gained if the object is sold at Rs 464. Find the selling price to get a profit of 10%
Answer: Rs 495
6.A shopkeeper sells an article for Rs 78 and earns double the profit that he would have earned had he sold it for Rs 69.What is the cost price ?
Answer: Rs 60
7. A man buys pencils at the rate of 6 for Rs 5 and sells them at 5 fo Rs 6. His profit percent is
Answer: 44%
8.Some toffees were bought at the rate fo 11 for Rs 10 and the same number at the rate of 9 for Rs 10. If the whole lot was sold at one rupee per toffee, then gain or loss in the whole transaction was
Answer: 1% loss
9.By selling 33m cloth a shopkeeper earns profit equivalent to selling price of 11m. Find his profit percentages?
Answer: 50%
10. By selling 33 m cloth, a shopkeeper loss money equivalent to selling price of 11m. Find his loss percentage
Answer: 25 %
11. By selling 33m cloth a shopkeeper earns profit equivalent to the cost price of 11 m. Find his selling profit percentage.
Answer: 33.33%
12. The cost price of 20 article is same as the selling price of 10 articles. The profit percent is
Answer: 100%
13.A dealer sold two bikes for Rs 7400 each. On one he gained 10% and on the other he lost 10%. The dealer's loss or gain in the transactions is
Answer: 1% loss
14. A dishonest shopkeeper sells goods at cost price but uses 800 gms in place of 1 Kg weight. Find his profit percent
Answer: 25%
15. The price of tea increases by 32% and so a housewife expenditure on tea increases by 10%. If she bought 10 kg earlier, what is the quantity bought now.
Answer: 8.33
16. A shopkeeper sells an article at 20% profit. Had he bought it for 10% less and sold it fo Rs 12 less, he would have earned 30% profit. What is the actual costs price.
Answer: Rs 400
17. A persons sells an article at a profit of 10%. If he had bought it at 10% less and sold it for Rs 3 more, he would have gains 25%. Find the cost price.
Answer:Rs 120
18. Mohit sold an article for Rs 1840 and made Rs 15 percent profit on the discounted price he bought. If the discount was 20% , what was the original price?
Answer: Rs.2000
19. A sold an article to B at the profit of 25%, B sold it to C at loss of 10% and C sold it to D at the profit of 20%. If D paid Rs 27 then how much A paid to buy article?
Answer:Rs 20
20. A person bought two watches for Rs 480. He sold one at a loss of 15% and the other at a profit of 19% and he found that each watch was sold at the same price.Find the cost price of two watches
Answer: Rs 280, Rs 200
21. At the marked price of 36 pens a retail seller buys 40 pens. If he gives 1% discount, find his profit percent
Answer: 105
22. 9 kg of rice cost as much as 4kg of sugar, 14 kg of sugar cost as much as 1.5 Kg of tea, 2 kg of tea cost as much as 5 kgs of coffee; find the cost of 11 kgs of coffee, if 2.5 kg of rice cost 12.50
Answer: Rs 462
23. A man buys some oranges at the rate of 5 for 1 and same number fo oranges at the rate of 4 for Rs 1. He sold all of them at the rate of 9 for Rs 2. During the whole transactions, he incurred a loss of Rs 30. Find the number of articles that he purchased.
Answer: Rs 10800
24. A shopkeeper promises to sell his goods at 10% profit but he uses a false weight of 205 less. Find his profit%
Answer: 37.5
25. A man purchases some oranges at the rate of 25 for 1. How many for Rs 1 should he sell to gain 25% profit.
Answer: 20
26. By selling 32 toffees for Rs 1 a man loses 40%. How many for Rs 1 did he sell to gain 20% profit
Answer:16
27. The profit % of A and B are same on selling the articles at Rs 1800 each but A calculated his profit on selling price and B calculated his profit on cost price which is equal to 20%.Find the total C.P
Answer: 2940
28. At what % above the C.P must an article be marked so as to gain 33% after allowing a customer a discount of 5%
Answer: 40%
Comments
Post a Comment